Difficulty: ★★☆☆☆
This document is from my notepad and a real-world implementation of the document(s) found at Archlinux Wiki - TigerVNC.
VNC
VNC is a protocol where you use your keyboard/mouse/screen to monitor or control a remote system.
![]()
![]()
VNC is per definition insecure
Opening a VNC service onto insecure networks like the internet, public libraries, internet cafès etc. may lead to information leaking and/or attempts to take control of your system.
This topic will only expose VNC to the localhost and use a secure connection using SSH.
For guidance with SSH - see [root tip] [How To] Set up your own SSH service.
The added benefit of using SSH is that you can easily adapt this example to target any remote server without sacrificing security.
TigerVNC Limitations
Multiple X sessions for a single user are not supported
– TigerVNC - ArchWiki
This effectively means - if you are logged onto the physical display :0 then you cannot connect a vnc session. If you try to do so, using the same username, a black screen or system lockup will be the likely result.
In that regard it works like Microsoft RDP which logout the physical session when you initiate a remote connection and vice-versa.
Target system
On the system to be controlled install package tigervnc
VNC password
Create a password for your login
vncpasswd
Configuration
Replace the phrase $USERNAME with the username of the actual user you want to configure.
List the available sessions
ls /usr/share/xsessions
Create the file /home/$USERNAME/.vnc/config with content (replace $SESSION according to your installation e.g. openbox or lxqt).
session=$SESSION
geometry=1280x720
localhost
dpi=96
Allow user on specific display
Edit /etc/tigervnc/vncserver.users and append e.g. :4 - which in turn will correspond to port 5904 - replace $USERNAME with the user you just created the password for.
:4=$USERNAME
Start a vncserver at the selected display
systemctl enable vncserver@:4
Logout or restart the device
reboot
Controlling system
Install the package tigervnc
Connect to target system
SSH provides a secure channel and using key based authentication is the recommended method.
Open a ssh connection using port mapping
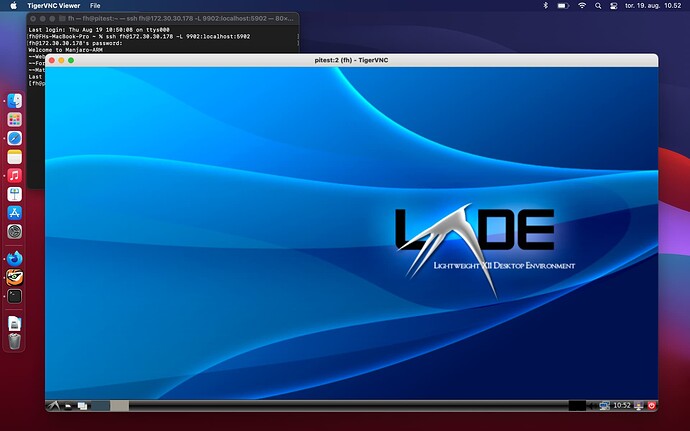
ssh $USERNAME@ip.x.y.z -L 9904:localhost:5904
Then launch the VNC viewer and input the following connection details and click connect
localhost:9904
Authenticate
Input the password created earlier (ignore the warning as we are using an encrypted connection) and you will see the remote system - which could just be a Raspberry Pi sitting next to you on the desk.